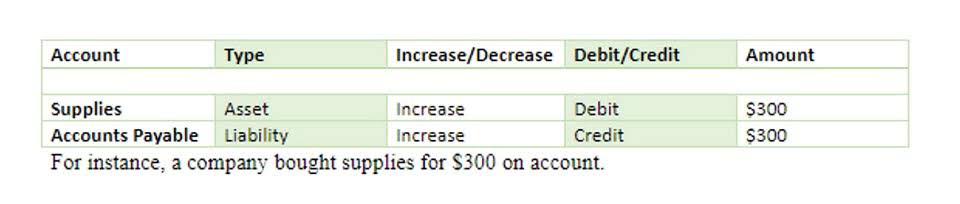
This can help prevent errors while also giving you a better understanding of the entire accounting process. Before you can begin to use a T-account, you have to understand some basic accounting terms. If that’s not the case, make sure to double-check your books as you’ve probably made an accounting error along the way. This feature allows you to focus on specific dimensions and gain insightful knowledge regarding the financial health of your business.
- Cash had a debit of $20,000 in the journal entry, so $20,000 is transferred to the general ledger in the debit column.
- In the Miscellaneous Expense T-Account, the $1,800 expense amount goes on the left (debit) side of the account because the expense is increasing.
- Under the generally accepted accounting principles, you do not have to follow an accounting standard if an item is immaterial.
- Notice that for this entry, the rules for recording journal entries have been followed.
- Some of the listed transactions have beenones we have seen throughout this chapter.
Service Revenue Earned and Collected
Another way to visualize business transactions is to write a general journal entry. Each general journal entry lists the date, the account title(s) to be debited and the corresponding amount(s) followed by the account title(s) to be credited and the corresponding amount(s). Let’s illustrate the general journal entries for supplies t account the two transactions that were shown in the T-accounts above.
How do you calculate the balance on a T-Account?
- Supplies are incidental items used during the course of production, or as part of an organization’s administrative activities.
- Common Stock hada credit of $20,000 in the journal entry, and that information istransferred to the general ledger account in the credit column.
- However, it records journal entries in a similar way.
- The general ledger is an accounting report that sorts and records a business’ financial transactions, by account.
- We’re firm believers in the Golden Rule, which is why editorial opinions are ours alone and have not been previously reviewed, approved, or endorsed by included advertisers.
- In the journal entry, Utility Expense has a debit balance of$300.
The main thing you need to know about debit and credit entries is that they are the equal and opposite sides of a financial transaction. They’re simply words representing where cash is coming from, and where it’s flowing to, within a business. Because T accounts are posted into the General Ledger of a business, they’re also commonly recognized as ledger accounts. A T-Account records the debits and credits that affect an account, as well as the running balance of the account. A revenue account that reports the sales of merchandise.

Journal Entries in Accounting (Explained) Practical Examples

Thesereports have much more information than the financial statements wehave shown you; however, if you read through them you may noticesome familiar items. We now return to our company example of Printing Plus, LynnSanders’ printing service company. We will analyze and record eachof the transactions for her business and discuss how this impactsthe financial statements. Some of the listed transactions have beenones we have seen throughout this https://www.bookstime.com/ chapter.
A summary showing the T-accounts for Printing Plus is presented in Figure 3.10. The following are selected journal entries from Printing Plus that affect the Cash account. We will use the Cash ledger account to calculate account balances. It is a good idea to familiarize yourself with the type of information companies report each year. Peruse Best Buy’s 2017 annual report to learn more about Best Buy. Take note of the company’s balance sheet on page 53 of the report and the income statement on page 54.

When calculating balances in ledger accounts, one must take into consideration which side of the account increases and which side decreases. To find the account balance, you must find the difference between the sum of all figures on the side that increases and the sum of all figures on the side that decreases. T-accounts are commonly used to prepare adjusting entries. The matching principle in accrual accounting states that all expenses must match with revenues generated during the period.
How much will you need each month during retirement?
Interest Revenues account includes interest earned whether or not the interest was received or billed. Interest Revenues are nonoperating revenues or income for companies not in the business of lending money. For companies in the business of lending money, Interest Revenues are https://www.facebook.com/BooksTimeInc/ reported in the operating section of the multiple-step income statement. Under the accrual basis of accounting, the Service Revenues account reports the fees earned by a company during the time period indicated in the heading of the income statement.
- More detail for each of these transactions is provided, along with a few new transactions.
- The date of each transaction related to this account is included, a possible description of the transaction, and a reference number if available.
- Thus, the T-account is used for the set of financial records that use double-entry bookkeeping.
- This is posted to the Dividends T-account on the debit side.
- Securities and Exchange Commission in 1999, any item representing five percent or more of a business’s total assets should be deemed material and listed separately on its balance sheet.
- For example, Accumulated Depreciation is a contra asset account, because its credit balance is contra to the debit balance for an asset account.
- This T format graphically depicts the debits on the left side of the T and the credits on the right side.
- T-accounts can also impact balance sheet accounts such as assets as well as income statement accounts such as expenses.
- The visual representation can be easier for beginners than just putting them straight in a line.
- Below is a short video that will help explain how T Accounts are used to keep track of revenues and expenses on the income statement.
- Each general journal entry lists the date, the account title(s) to be debited and the corresponding amount(s) followed by the account title(s) to be credited and the corresponding amount(s).
- This is posted to the Cash T-account on the credit side.
It can be used to balance books by adding all transactions in a set of accounts so the total debits equal the total credits for each account. A temporary account used in the periodic inventory system to record the purchases of merchandise for resale. (Purchases of equipment or supplies are not recorded in the purchases account.) This account reports the gross amount of purchases of merchandise. Net purchases is the amount of purchases minus purchases returns, purchases allowances, and purchases discounts.